前言
本文是南京大学李樾、谭添老师的《软件分析》课程的笔记。内容来自课程ppt以及课程讲解。
课程主页:Static Program Analysis | Tai-e (pascal-lab.net)
授课视频:视频南京大学《软件分析》课程01(Introduction)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
课程实验repo:pascal-lab/Tai-e-assignments: Tai-e assignments for static program analysis (github.com)
Contents
- Overview of Data Flow Analysis
- Preliminaries of Data Flow Analysis
- Reaching Definitions Analysis
- Live Variables Analysis
- Available Expressions Analysis
Live Variables Analysis
Live Variables Analysis
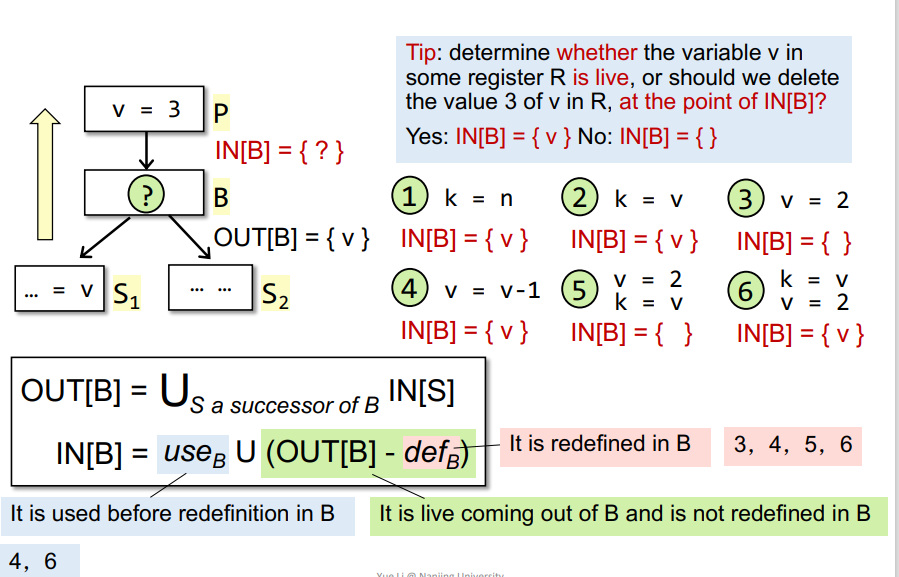
Live variables analysis tells whether the value of variable v at program point p could be used along some path in CFG starting at p. If so, v is live at p; otherwise, v is dead at p.
- Information of live variables can be used for register allocations. e.g., at some point all registers are full and we need to use one, then we should favor using a register with a dead value.

Understanding Live Variables Analysis
Abstraction
Data Flow Values/Facts
All the variables in a program
Can be represented by bit vertors
e.g., V1, V2, V3, V4, …, V100(100 variables)
$\underbrace{0000…0}_{100}$
Bit i from the left represents variable Vi
Safe-approximation
Algorithm of Live Variables Analysis
INPUT: CFG($def_B$ and $use_B$ computed for each basic block B)
OUTPUT: $IN[B]$ and $OUT[B]$ for each basic block B
METHOD: 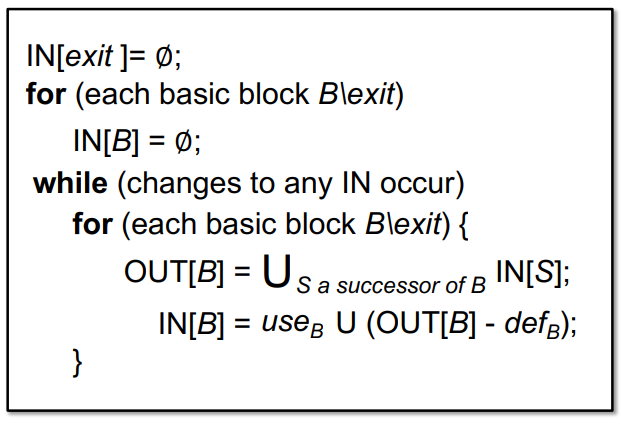
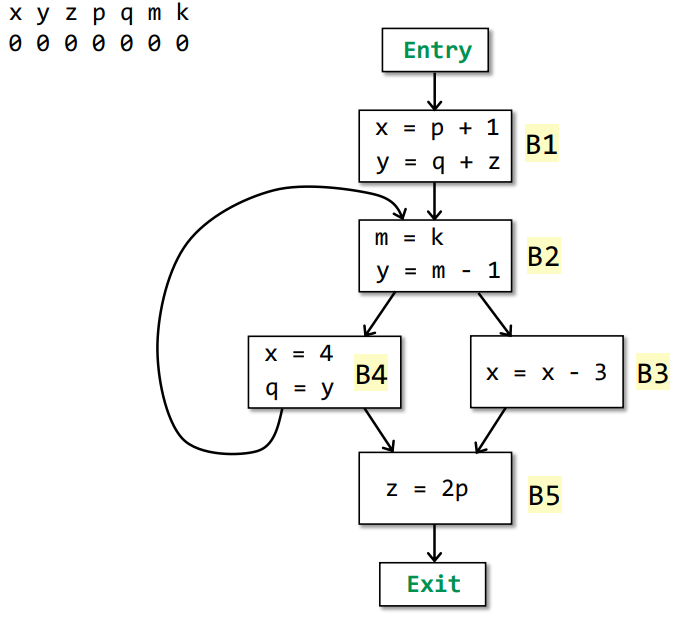
Example
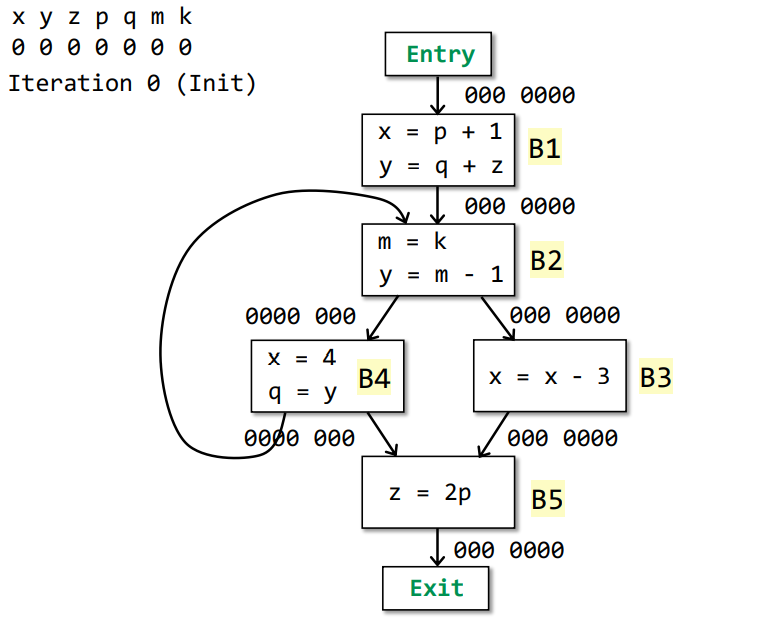
Iteration 0(Init)
| OUTPUT | use | def | INPUT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exit | 000 0000 | |||
| B5 | 000 0000 | |||
| B4 | 000 0000 | |||
| B3 | 000 0000 | |||
| B2 | 000 0000 | |||
| B1 | 000 0000 |
Iteration 1
| OUTPUT | use | def | INPUT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exit | 000 0000 | |||
| B5 | 000 0000 | p | z | 000 1000 |
| B4 | 000 0000 U 000 1000 | y | x q | 010 1000 |
| B3 | 000 1000 | x | 100 1000 | |
| B2 | 010 1000 U 100 1000 | k | m y | 100 1001 |
| B1 | 100 1001 | p q z | y x | 001 1101 |
Changes occur in IN[] of B1, B2, B3, B4, B5
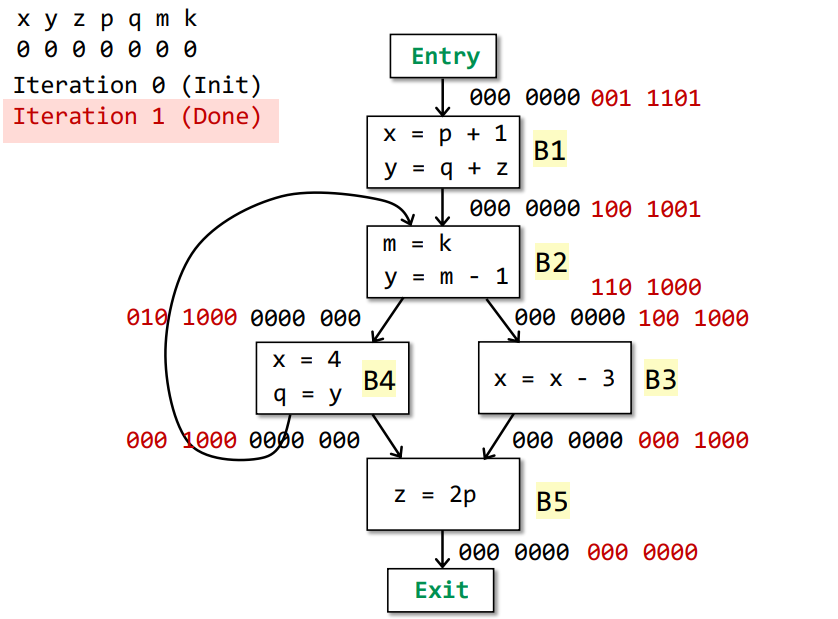
Iteration 2
| OUTPUT | use | def | INPUT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exit | 000 0000 | |||
| B5 | 000 0000 | p | z | 000 1000 |
| B4 | 100 1001 U 000 1000 | y | x q | 010 1001 |
| B3 | 000 1000 | x | 100 1000 | |
| B2 | 010 1001 U 100 1000 | k | m y | 100 1001 |
| B1 | 100 1001 | p q z | y x | 001 1101 |
Changes orrcur in IN[] of B4
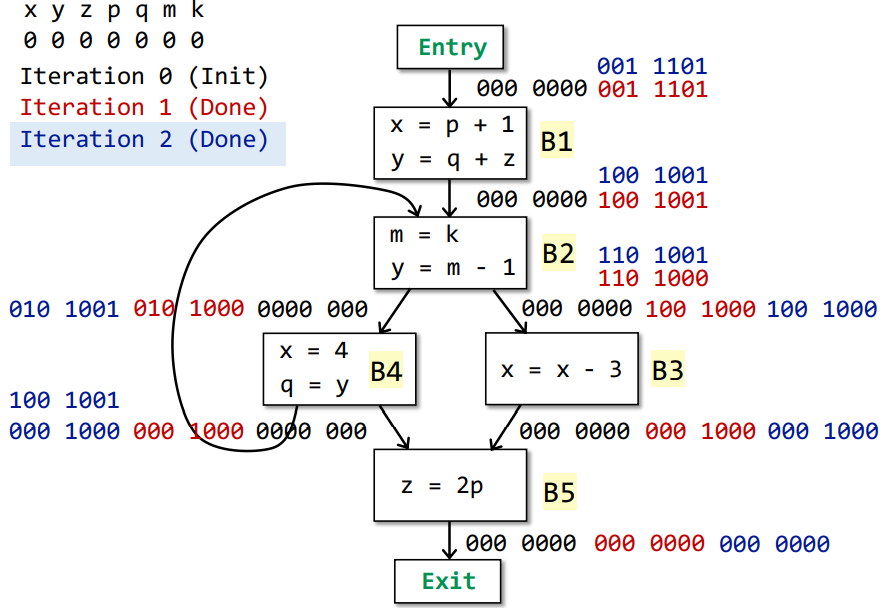
Iteration 3
| OUTPUT | use | def | INPUT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exit | 000 0000 | |||
| B5 | 000 0000 | p | z | 000 1000 |
| B4 | 100 1001 U 000 1000 | y | x q | 010 1001 |
| B3 | 000 1000 | x | 100 1000 | |
| B2 | 010 1001 U 100 1000 | k | m y | 100 1001 |
| B1 | 100 1001 | p q z | y x | 001 1101 |
No changes occur in any IN[]
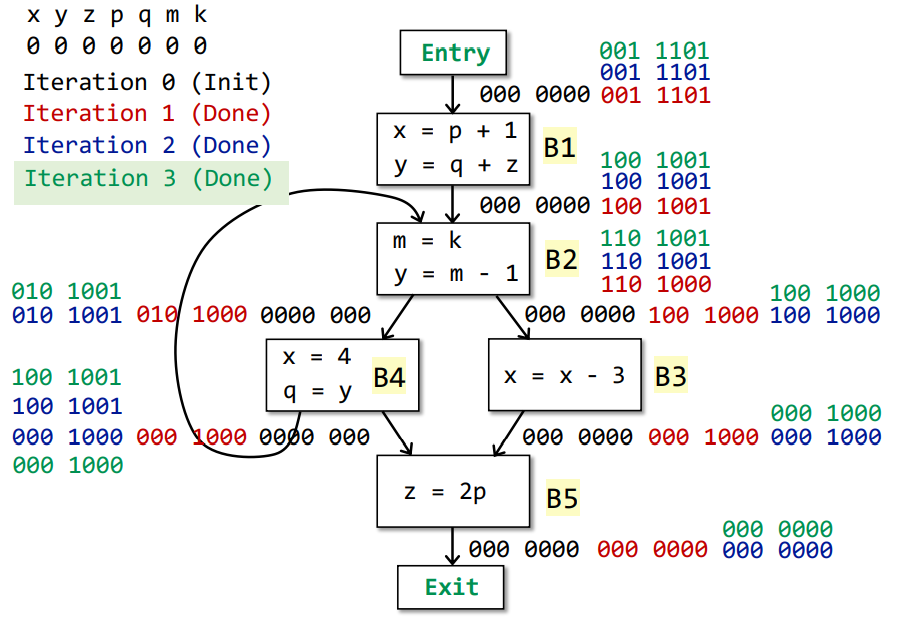
Avaliable Expression Analysis
Avaliable Expression Analysis
An expression x op y is available at program point p if (1) all paths from the entry to p must pass through the evaluation of x op y, and (2) after the last evaluation of x op y, there is no redefinition of x or y
- This definition means at program p, we can replace expression x op y by the result of its last evaluation
- The information of available expressions can be used for detecting global common subexpressions
Understanding Avaliable Expression Analysis
Abstraction
Data Flow Values/Facts
All the expressions in a program
Can be represented by bit vectors
e.g., E1, E2, E3, E4, …, E100 (100 expressions)
$\underbrace{0000…0}_{100}$
Bit i from the left represents expression Ei
Safe-approximation
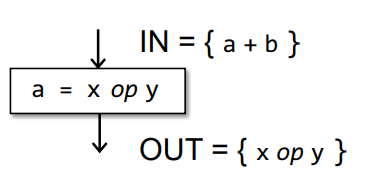
- Add to OUT the expression x op y(gen)
- Delete from IN any expression involving variable a(kill)
$OUT[B] = gen_B \cup(IN[B] - kill_B)$
$IN[B] = \cap_{P~a~predecessor~of~B }OUT[P]$
$\cap$ : All paths from entry to point p must pass through the evaluation of x op y
For safety of the analysis, it may report an expression as unavailable even if it is availabe(must analysis -> under-approximation)
Algorithm of Avaliable Expressions Analysis
INPUT: CFG($kill_B$ and $gen_B$ computed for each basic block B)
OUTPUT: IN[B] and OUT[B] for each basic block B
METHOD: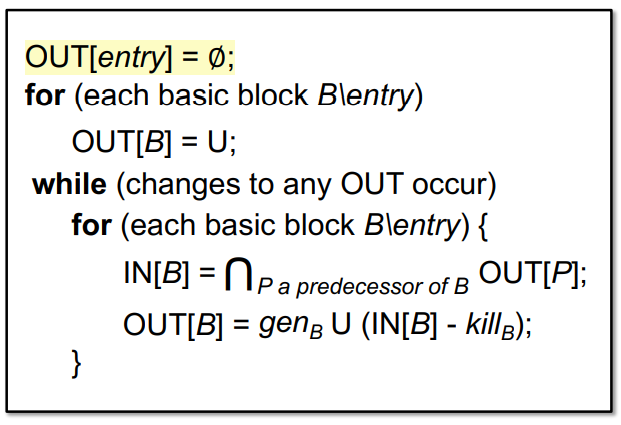
Example
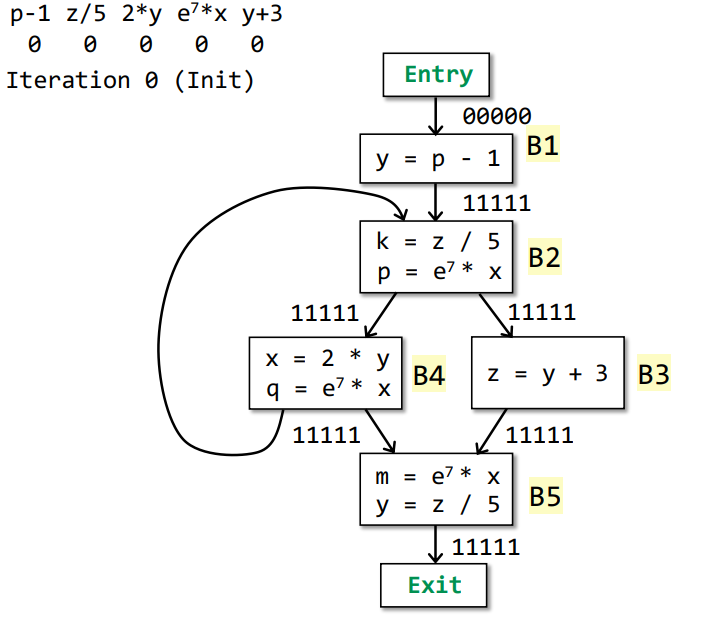
Iteration 0(Init)
| INPUT | gen | kill | OUTPUT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | 00000 | |||
| B1 | 11111 | |||
| B2 | 11111 | |||
| B3 | 11111 | |||
| B4 | 11111 | |||
| B5 | 11111 |
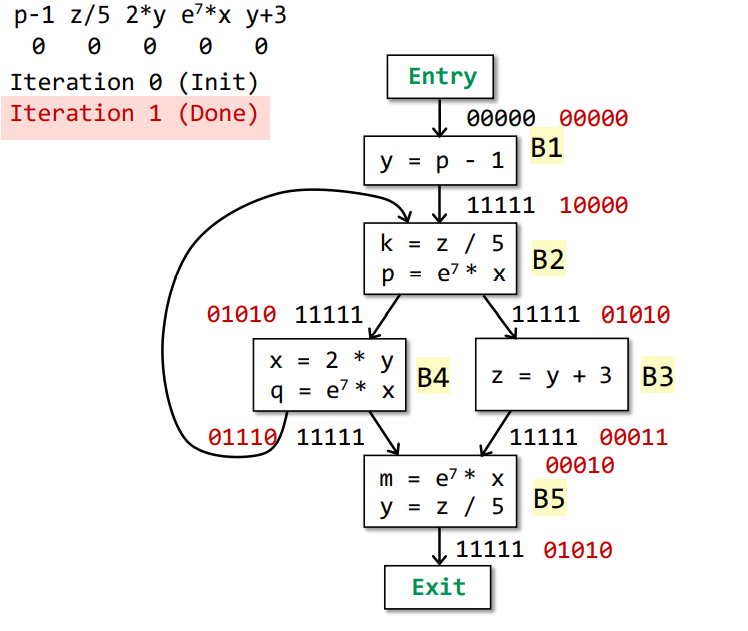
Iteration 1
| INPUT | gen | kill | OUTPUT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | 00000 | |||
| B1 | 00000 | p-1 | y | 10000 |
| B2 | 11111 $\cap$ 10000 | z/5 $e^7*x$ | k,p | 01010 |
| B3 | 01010 | y + 3 | z | 00011 |
| B4 | 01010 | 2*y $e^7*x$ | x q | 01110 |
| B5 | 00011 $\cap$ 01110 | $e^7*x$ z/5 | m y | 01010 |
Changes occur in OUT[] of B1 B2 B3 B4 B5
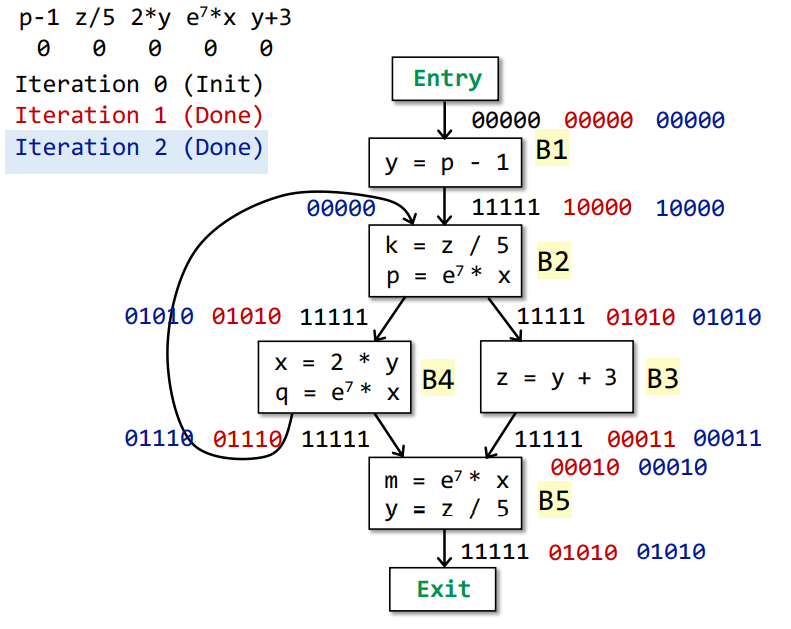
Iteration 2
| INPUT | gen | kill | OUTPUT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | 00000 | |||
| B1 | 00000 | p-1 | y | 10000 |
| B2 | 01110 $\cap$ 10000 | z/5 $e^7*x$ | k,p | 01010 |
| B3 | 01010 | y + 3 | z | 00011 |
| B4 | 01010 | 2*y $e^7*x$ | x q | 01110 |
| B5 | 00011 $\cap$ 01110 | $e^7*x$ z/5 | m y | 01010 |
No changes occur in any OUT[]
Analysis Comparison
| Reaching Definitions | Live Variables | Available Expressions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | Set of definitions | Set of variables | Set of expressions |
| Direction | Forwards | Backwards | Forwards |
| Mat/Must | May | May | Must |
| Boundary | $OUT[entry]=\phi$ | $IN[exit]=\phi$ | $OUT[entry]=\phi$ |
| Initialization | $OUT[B]=\phi$ | $IN[B]=\phi$ | $OUT[B]=\cup$ |
| Transfer function | $OUT=gen\cup(IN-kill)$ | - | - |
| Meet | $\cup$ | $\cup$ | $\cap$ |