1.基本概念
1.1 前沿
web开发:
- web,网页的意思
- 静态web
- html,css
- 提供给所有人看的数据始终不会发生变化
- 动态web
- 淘宝
- 每个人不同时间不同地点看到的信息各不相同
- 技术栈:Servlet/ISP ASP PHP
在Java中,动态web资源开发的技术统称为JavaWeb
1.2 web应用程序
web应用程序,可以提供浏览器访问的程序
- a.html b.html……多个web资源,这些web可以被外界访问,对外界提供服务
- 能访问到的任意一个页面或者资源,都存在于某个计算机上
- URL
- 这个统一的web资源会被放在同一个文件夹下,web应用程序->Tomcat:服务器
- 一个web应用由多部分组成(静态web,动态web)
- html css js
- jsp servlet
- Java
- jar包
- 配置文件(Properties)
web应用程序编写完毕后,若想提供给外界访问,需要一个服务器统一管理
1.3 静态web
.htm .html都是网页的后缀,如果服务器上一直存在这些东西,就可以直接进行读取,通信

静态web存在的缺点
- Web页面无法动态更新,所有用户看到的都是同一个页面
- 轮播图 点击特效:伪动态
- JavaScript(实际开发最常用)
- VBScript
- 无法与数据库交互(数据无法持久化,用户无法交互)
- Web页面无法动态更新,所有用户看到的都是同一个页面
1.4 动态web
页面会动态显示,Web的页面显示效果因人而异

缺点
- 假如服务器的动态web资源出现了错误,需要重写后台程序,重新发布
- 停机维护
优点
静态web存在的缺点
- Web页面可以动态更新,所有用户看到的不是同一个页面
- 可以与数据库交互

2 Web服务器
2.1 技术讲解
ASP
- 微软:国内最早流行的就是ASP
- 在HTML中嵌入了VB的脚本,ASP+COM;
- 在ASP开发中,基本上每一个页面都有几千行的业务代码,页面及其混乱
- 维护成本高
php
- PHP开发速度很快,功能强大,跨平台,代码简单
- 无法承载大访问量的情况(局限性)
JSP/Servlet
- SUN公司主推的B/S架构
- 基于Java语言
- 可以承载三高问题带来的影响
- 语法像ASP
2.2 Web服务器
服务器是一种被动的操作,用来处理用户的一些请求,给用户相应信息
IIS:微软,ASP Windows中自带的
Tomcat:Tomcat是Apache 软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目,最新的Servlet 和JSP 规范总是能在Tomcat 中得到体现。因为Tomcat 技术先进、性能稳定,而且免费,因而深受Java 爱好者的喜爱并得到了部分软件开发商的认可,成为目前比较流行的Web 应用服务器。
Tomcat 服务器是一个免费的开放源代码的Web 应用服务器,属于轻量级应用服务器,在中小型系统和并发访问用户不是很多的场合下被普遍使用,是开发和调试JSP 程序的首选。对于一个初学JavaWeb的人来说,它是最佳选择
Tomcat 实际上运行JSP 页面和Servlet。目前Tomcat最新版本为9.0.37。
下载tomcat:
- 安装/解压
- 了解配置文件及目录结构
- 了解作用
3 Tomcat
3.1 安装Tomcat
3.2 启动和配置
文件夹:

启动,关闭Tomcat
bin>startup.bat / shutdown.bat
访问测试: http://localhost:8080/
3.3 配置

可以配置启动的端口号
- Tomcat的默认端口号:8080
- MySQL:3306
- http:80
- https:443
1 | <Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" |
可以配置主机的名称
- 默认的主机名:localhost ->127.0.0.1
- 默认的网站应用存放的位置:webapps
1 | <Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps" |
面试题
访问网页流程:
- 输入域名
- 检查本机的hosts配置文件下有没有这个域名映射
- 有,直接放回对应的ip地址,在这个地址中,有需要访问的web程序,可以直接访问
- 没有:去DNS解析

3.4 发布web网站
- 将自己写的网站放到服务器(Tomcat)中指定的web应用文件夹(webapps)下
网站应有的结构
1 | -- webapps :Tomcat服务器的web目录 |
4.Http
4.1什么是http
http(超文本传输协议)是一个简单的请求-响应协议,它通常运行在TCP之上。
- 文本:html,字符串,……
- 超文本:图片,音乐,视频,地图,定位……
- 端口 80
https:s—-安全的
- 443
4.2 两个时代
Http1.0
- HTTP/1.0:客户端可以与web服务器连接后,只能获得一个web资源
- Http2.0
- HTTP/1.1:客户端可以与web服务器连接后,可以获得多个web资源
4.3 Http请求
- 客户端—发请求—服务器
百度
1 | Request URL:https://www.baidu.com/ 请求地址 |
- 请求行
- 请求行中的请求方式:GET
- 请求方式:Get,Post,HEAD,DELETE,PUT,TRACT.…
- get:请求能够携带的参数比较少,大小有限制,会在浏览器的URL地址栏显示数据内容,不安全,但高效
- post:请求能够携带的参数没有限制,大小没有限制,不会在浏览器的URL地址栏显示数据内容,安全,但不高效。
- 消息头
1 | Accept:告诉浏览器,它所支持的数据类型 |
4.4 Http响应
- 服务器—响应—客户端
百度
1 | Cache-Control:private 缓存控制 |
- 响应体
1 | Accept:告诉浏览器,它所支持的数据类型 |
- 响应状态码
200:请求响应成功200
3xx:请求重定向
- 重定向:你重新到我给你新位置去;
4xx:找不到资源404
- 资源不存在;
5xx:服务器代码错误 500 502:网关错误
常见面试题:
当浏览器中地址栏输入地址并回车到页面展示,经历了什么?
5 Maven
为什么学习Maven?
- 在JavaWeb开发中,需要使用大量的的jar包,需要手动导入
- 如何自动导入和配置jar包?Maven
5.1 Maven项目架构管理工具
目的:方便导入jar包
Maven核心思想:约定大于配置
- 有约束,不要去违反
Maven会规定要如何去编写Java代码,必需按规范来。
5.2 下载安装Maven
5.3配置环境变量
- M2_HOME maven目录下的bin目录
- MAVEN_HOME maven的目录
- 在系统的path中配置%MAVEN_HOME%\bin
5.4 阿里云镜像
- 镜像:mirrors
- 作用:加速我们的下载
- 国内建议使用阿里云的镜像
1 | <mirror> |
5.5 本地仓库
在本地的仓库,远程仓库; 建立一个本地仓库:localRepository
1 | <localRepository>D:\apache-maven-3.6.1\maven-repo</localRepository> |
5.6 在IDEA中使用Maven
- 启动IDEA
- 创建Maven项目



- 自动导入包

- 观察Maven仓库多了什么东西?
- IDEA中的Maven设置

注意:项目创建完成后,IDEA有时候会选择默认的Maven,要切换成本地的
- 到这里,Maven在IDEA中的配置和使用就OK了。
5.7 创建空的Maven项目
5.8 标记文件夹功能


5.9 在IDEA中配置Tomcat




点击启动

5.10 pom文件
pom.xml是Maven的核心配置文件
maven由于约定大于配置,之后可能遇到写的配置文件无法被导出或者生效的问题,
1 | <build> |
6 Servlet
6.1 Servlet简介
- Servlet就是sun公司开发动态web的一门技术
- Sun在这些API中提供了一个接口叫Servlet,如果想开发Servlet,只需要
- 编写类,实现Servlet接口
- 把开发好的java类部署到web服务器中
把实现了Servlet接口的Java程序叫做Servlet
6.2 HelloServlet
Servlet接口有两个默认的实现类,HttpServlet,GenericServlet
创建普通Maven项目,删除src,在里面建立Module
关于Maven父子工程的理解:
父项目中会有
1
2
3<modules>
<module>servlet-01</module>
</modules>子项目里会有
1
2
3
4
5<parent>
<artifactId>javaweb-02-servlet</artifactId>
<groupId>com.zz</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
Maven环境优化
修改web.xml为最新的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0"
metadata-complete="true">
</web-app>
- 将Maven的结构搭建完整
编写一个Servlet程序
- 编写一个普通类
- 实现Servlet接口,继承HttpServlet
1 | public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { |
编写Servlet映射
为什么需要映射?写的是Java程序,但是要通过浏览器访问,浏览器需要连接web服务器,所以需要在web服务器中注册Servlet,还需给它一个浏览器能够访问的路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10<!--注册servlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.zz.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!--请求路径-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>配置Tomcat
启动测试
6.3 Servlet原理
Servlet是由Web服务器调用,web服务器在收到浏览器请求之后,会:

6.4 Mapping
一个Servlet可以指定一个映射路径
1
2
3
4<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
一个Servlet可以指定多个映射路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello3</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello4</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello5</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>一个Servlet可以指定通用映射路径
1
2
3
4<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>默认请求
1
2
3
4
5<!--默认请求路径-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
指定一些后缀或者前缀
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8<!--可以自定义后缀实现请求映射
注意点,*前面不能加项目映射的路径
hello/sajdlkajda.qinjiang
-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.qinjiang</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>优先级问题:
指定了固有的映射路径优先级最高,如果找不到就会走默认的处理请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11<!--注册servlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>error</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.zz.servlet.ErrorServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!--请求路径-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>error</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
6.5 ServletContext
web容器在启动的时候,它会为每个web程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表了当前的web应用;
1.共享数据
我再这个Servlet中保存的数据,可以在另一个servlet中拿到
放数据:
1 | public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { |
读数据
1 | public class GetServlet extends HttpServlet { |
2.获取初始化参数
1 | <!--配置web初始化参数--> |
1 | public class ServletDemo03 extends HttpServlet { |
3.请求转发
1 | public class ServletDemo04 extends HttpServlet { |
重定向与转发:

4.读取资源文件
Properties
- 在java目录下新建properties
- 在resources目录下新建properties
发现都被打包到了同一个路径下:classes,俗称classpath
思路:需要一个文件流
1 | public class ServletDemo05 extends HttpServlet { |
6.6 HttpServletResponse
web服务器接收到客户端的http请求,针对这个请求,分别创建一个代表请求的HttpServletRequest对象和一个代表响应的HttpServletResponse对象
- 如果要获取客户端请求过来的参数 :找HttpServletRequest
- 如果要给客户端响应一些信息,找HttpServletResponse
1.简单分类
负责向浏览器发送数据的方法
1 | servletOutputstream getOutputstream() throws IOException; |
负责向浏览器发送响应头的方法
1 | void setCharacterEncoding(String var1); |
响应的状态码
1 | int SC_OK = 200; |
2.常见应用
向浏览器输出消息
下载文件
- 要获取下载文件的路径
- 下载的文件名
- 下载的文件名设置想办法让浏览器支持下载需要的东西
- 获取下载文件的输入流
- 创建缓冲区
- 获取OutputStream对象
- 将FileOutputStream流写入到buffer缓冲区
- 使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的数据输出到客户端
验证码
验证码怎么来的?
- 前端实现
- 后端实现,需要用到java的图片类,生成图片
重定向

一个web资源收到客户端请求后,他会通知A客户端去访问另一个web资源C,这个过程叫重定向
常见场景
- 用户登录
1 | public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet { |
重定向和转发的区别?
相同点:
- 页面都会发生变化
不同点:
- 请求转发的时候,url不会发生变化
- 重定向的时候,url地址会发生变化
index.jsp
1 | <html> |
RequestTest
1 | public class RequestTest extends HttpServlet { |
6.7 HttpServletRequest
HttpServletRequest代表客户端的请求,用户通过Http协议访问服务器,Http请求中的所有信息会被封装到HttpServletRequest,通过这个HttpServletRequest的方法,获得客户端的所有信息


1.获取前端的参数

1 | package com.zz.request; |
重定向和转发的区别?
相同点:
- 页面都会发生变化
不同点:
- 请求转发的时候,url不会发生变化 307
- 重定向的时候,url地址会发生变化 302
7 Cookkie、Session
7.1 会话
会话:用户打开一个浏览器,点击了很多超链接,访问多个web资源,关闭浏览器,这个过程可以成为会话
有状态会话:一个同学来过教室,下次再来,就会知道他曾经来过
如何证明是学生?
学生 学校
- 发票 学校给学生发票
- 学校登记 学校标记学生来过
一个网站,如何证明来过?
客户端 服务端
- 服务端给客户端一个信件,客户端下次访问服务端带上信件就可以了;cookie
- 服务器登记你来过了,下次来服务器来匹配;session
7.2保存会话的两种技术
cookie
- 客户端技术(响应,请求)
session
- 服务器技术,利用这个技术,可以保存用户信息。可以把信息或者数据放在Session中
常见应用:网站登录之后,下次就不用再登录了
7.3 Cookie
- 从请求中拿到cookie信息
- 服务器给客户端响应cookie
1 | Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();//获得cookie |
cookie:一般回保存在本地的用户目录下 appdata;
一个网站的cookie是否存在上限
- 一个cookie只能保存一个信息;key-value
- 一个web站点可以给浏览器发送多个cookie,最多存放20个cookie
- cookie大小有限制 4kb
- 浏览器上限 300个cookie
删除Cookie:
- 不设置有效期,关闭浏览器,自动失效
- 设置有效期时间为0
编码解码
1 | Cookie cookie = new Cookie("name", URLEncoder.encode("黑怕","utf-8")); |
7.4 Session(重点)
什么是Session:
- 服务器会给每一个用户(浏览器)创建一个Session对象
- 一个Seesion独占一个浏览器,只要浏览器没有关闭,这个session就存在
- 用户登录之后,整个网站都可以访问—>保存用户信息
1 | //得到session |
Session与Cookie的区别
- Cookie 把用户的数据写给用户的浏览器,浏览器保存
- Session把用户的数据写道用户独占的Session中,服务器端保存(保存重要的信息,减少服务器资源的浪费)
- Session对象由服务器创建
使用场景:
- 保存登录用户的信息
- 购物车
- 整个网站中经常使用的数据保存在session中
会话自动过期
1 | <!--设置session默认的失效时间--> |
Cookie:

Session

ServletContext

8 JSP
8.1 什么是JSP
Java Server Pages:Java服务器端页面,也和Servlet一样,用于动态Web技术!
最大的特点:
JSP就像HTML
区别
- HTML只给用户提供静态的数据
- jsp页面中可以嵌入Java代码,为用户提供动态数据
8.2 JSP原理
思路:JSP是怎么执行的?
代码层面:与HTML相同
服务器内部工作
tomcat中有一个work目录
IDEA中使用tomcat会在IDEA的tomcat中生成一个work目录
浏览器向服务器发送请求,不管访问什么资源,其实都是在访问Servlet
JSP最终也会被转换成一个Java类
JSP本质实就是一个Servlet
1 | //初始化 |
- 判断请求
- 内置了一些对象
1 | final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; //页面上下文 |
- 输出页面前增加的代码
1 | response.setContentType("text/html"); //设置响应的页面类型 |
- 以上的这些个对象我们可以在JSP页面中直接使用!
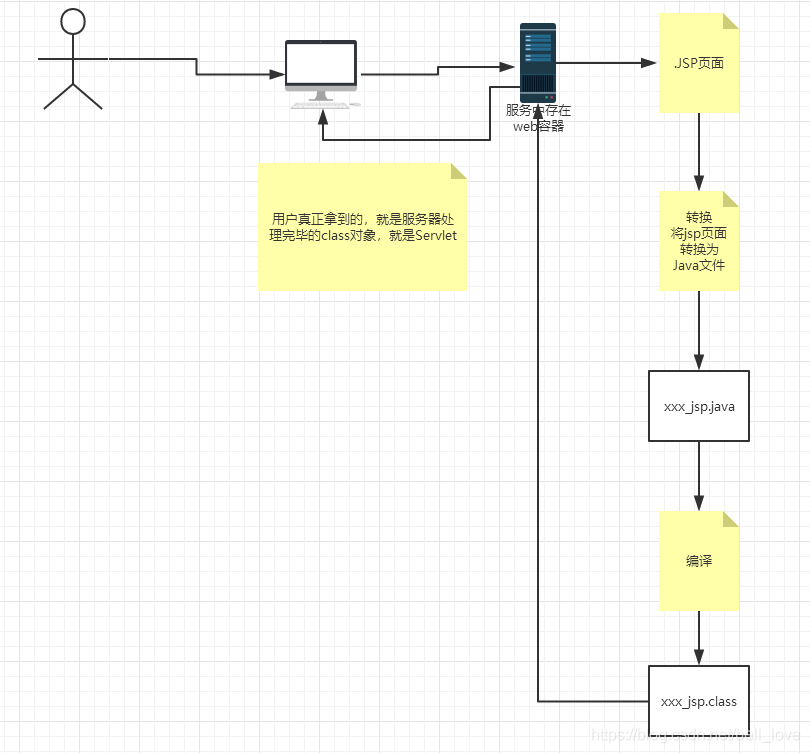
在JSP页面中;
只要是 JAVA代码就会原封不动的输出;
如果是HTML代码,就会被转换为:
1 | out.write("<html>\r\n"); |
输出到前端
8.3、JSP基础语法
任何语言都有自己的语法,JAVA中有,。 JSP 作为java技术的一种应用,它拥有一些自己扩充的语法(了解,知道即可!),Java所有语法都支持!
1 | <%--JSP表达式 |
jsp脚本片段
1 | <%--jsp脚本片段--%> |
脚本片段的再实现
1 | <% |
JSP声明
1 | <%! |
JSP声明:会被编译到JSP生成Java的类中!其他的,就会被生成到_jspService方法中!
在JSP,嵌入Java代码即可!
1 | <%%>//中间写java代码 |
JSP的注释,不会在客户端显示,HTML的会!
8.4 JSP指令
1 | <% args.... %> |
8.5 9大内置对象
PageContext 存东西
Request 存东西
Response
Session 存东西
Application 【SerlvetContext】 存东西
config 【SerlvetConfig】
out
page ,不用了解
exception
```java
pageContext.setAttribute(“name1”,”zz1”);//保存的数据只在一个页面中有效
request.setAttribute(“name2”,”zz2”); //保存的数据只在一次请求中有效,请求转发会携带这个数据
session.setAttribute(“name3”,”zz3”); //保存的数据只在一次会话中有效,从打开浏览器到关闭浏览器
application.setAttribute(“name4”,”zz4”); //保存的数据只在服务器中有效,从打开服务器到关闭服务器1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
request:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了,比如:新闻,用户看完没用的!
session:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户用完一会还有用,比如:购物车;
application:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,一个用户用完了,其他用户还可能使用,比如:聊天数据;
## 8.6、JSP标签、JSTL标签、EL表达式
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl-api</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
EL表达式: ${ }
- 获取数据
- 执行运算
- 获取web开发的常用对象
JSP标签
1 | <%--jsp.include--%> |
JSTL表达式
JSTL标签库的使用就是为了弥补HTML标签的不足;它自定义许多标签,可以供我们使用,标签的功能和Java代码一样!
格式化标签
SQL标签
XML 标签
核心标签 (掌握部分)

JSTL标签库使用步骤
- 引入对应的 taglib
- 使用其中的方法
- 在Tomcat 也需要引入 jstl的包,否则会报错:JSTL解析错误
c:if
1 | <h4>if测试</h4> |
c:choose c:when
1 | <c:set var="score" value="85"/> |
c:forEach
1 | <% |
9 JavaBean
实体类
JavaBean有特定的写法:
- 必须要有一个无参构造
- 属性必须私有化
- 必须有对应的get/set方法;
一般用来和数据库的字段做映射 ORM;
ORM :对象关系映射
- 表—>类
- 字段–>属性
- 行记录——>对象
| id | name | age | address |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | zz1 | 3 | 西安 |
| 2 | zz2 | 18 | 西安 |
| 3 | zz3 | 100 | 西安 |
1 | class People{ |
10、MVC三层架构
- 什么是MVC: Model view Controller 模型、视图、控制器
10.1 以前的架构

用户直接访问控制层,控制层就可以直接操作数据库;
1 | servlet--CRUD-->数据库 |
10.2、MVC三层架构

Model
- 业务处理 :业务逻辑(Service)
- 数据持久层:CRUD (Dao - 数据持久化对象)
View
- 展示数据
- 提供链接发起Servlet请求 (a,form,img…)
Controller (Servlet)
- 收用户的请求 :(req:请求参数、Session信息….)
- 交给业务层处理对应的代码
- 控制视图的跳转
1 | 登录--->接收用户的登录请求--->处理用户的请求(获取用户登录的参数,username,password)---->交给业务层处理登录业务(判断用户名密码是否正确:事务)--->Dao层查询用户名和密码是否正确-->数据库 |
11 Filter (重点)
比如 Shiro安全框架技术就是用Filter来实现的
Filter:过滤器 ,用来过滤网站的数据;
- 处理中文乱码
- 登录验证….

Filter开发步骤:
导包
编写过滤器
导包不要错 (注意)

实现接口,重写对应方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23public class CharatorEncodingFilter implements Filter {
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("init");
}
// chain 链
/*
* 1 过滤器中所有的代码,在过滤特定请求的时候都会执行
* 2 必须要让过滤器继续通行
* */
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
servletRequest.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
servletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
servletResponse.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTG-8");
System.out.println("执行前");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);//让请求继续,如果不写就停止了
System.out.println("执行后");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
}- 在xml配置Filter
12 监听器
实现一个监听器的接口;(有n种监听器)
编写一个监听器
实现监听器的接口…
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44package com.zz.listener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener;
public class OnlineCountListener implements HttpSessionListener {
//创建session监听 看你的一举一动
//一旦创建session就会触发一次这个事件
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) {
System.out.println(se.getSession().getId());
ServletContext context = se.getSession().getServletContext();
Integer onlineCount = (Integer) context.getAttribute("OnlineCount");
if(onlineCount==null){
onlineCount = new Integer(1);
}else{
int i = onlineCount.intValue();
onlineCount = new Integer(i + 1);
}
context.setAttribute("OnlineCount",onlineCount);
}
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) {
ServletContext context = se.getSession().getServletContext();
Integer onlineCount = (Integer) context.getAttribute("OnlineCount");
if(onlineCount==null){
onlineCount = new Integer(0);
}else{
int i = onlineCount.intValue();
onlineCount = new Integer(i - 1);
}
context.setAttribute("OnlineCount",onlineCount);
}
/*
Session销毁:
1. 手动销毁 getSession().invalidate();
2. 自动销毁
*/
}xml注册监听器
1
2
3<listener>
<listener-class>com.zz.listener.OnlineCountListener</listener-class>
</listener>看情况是否使用
13 过滤器、监听器常见应用
监听器:GUI编程中经常使用;
1 | public class TestPanel { |
用户登录之后才能进入主页!用户注销后就不能进入主页了!
- 用户登录之后,向Sesison中放入用户的数据
- 进入主页的时候要判断用户是否已经登录;要求:在过滤器中实现!
1 | HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; |
14 JDBC
什么是JDBC : Java连接数据库!

需要jar包的支持:
- java.sql
- javax.sql
- mysql-conneter-java… 连接驱动(必须要导入)
实验环境搭建
1 | CREATE TABLE users( |
导入数据库依赖
1 | <!--mysql的驱动--> |
JDBC 固定步骤:
- 加载驱动
- 连接数据库,代表数据库
- 向数据库发送SQL的对象Statement : CRUD
- 编写SQL (根据业务,不同的SQL)
- 执行SQL
- 关闭连接(先开的后关)
1 | public class TestJdbc { |
事务
要么都成功,要么都失败!
ACID原则:保证数据的安全。
1 | 开启事务 |
Junit单元测试
依赖
1 | <!--单元测试--> |
简单使用
@Test注解只有在方法上有效,只要加了这个注解的方法,就可以直接运行!
1 |
|
搭建环境
1 | CREATE TABLE account( |
Reference
B站: 狂神说Java https://space.bilibili.com/95256449/